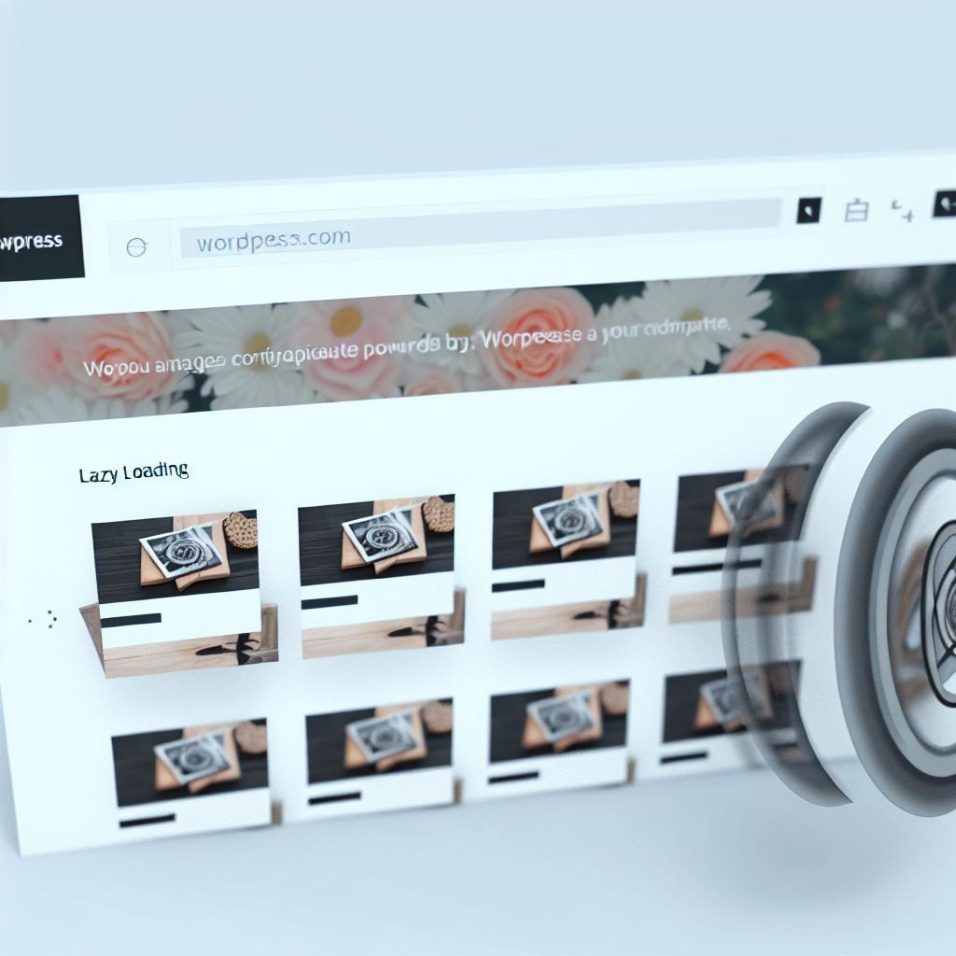
Understanding the Mechanism of Lazy Loading
Lazy loading leverages browser support to defer the loading of non-essential resources until they are actually needed. This approach is based on the Intersection Observer API, a modern browser feature designed to asynchronously observe changes in the intersection of a target element. By implementing lazy loading with minimal overhead, your website remains efficient and responsive, particularly when dealing with rich multimedia content.
How Lazy Loading Works
Lazy loading works by employing JavaScript to detect when an image or other media element is nearing the viewport. As it approaches, the resource loads on-demand, freeing up bandwidth for more immediate components of the page. Utilizing this smart, event-driven approach inline with modern web practices, lazy loading ensures that resources are allocated effectively, benefitting both page load performance and server bandwidth.
JavaScript and Browsers
Though native lazy loading through the `loading=”lazy”` attribute is supported in most modern browsers, other techniques may utilize a combination of custom JavaScript and CSS for more complex scenarios. This approach can offer a greater degree of customization, allowing developers to tailor lazy loading strategies to their specific use cases and audience’s browsing habits.
Extending Lazy Loading Beyond Images
While images are the most common element subjected to lazy loading, this strategy can be extended to videos, iframes, and even scripts. By prioritizing essential content, lazy loading optimizes page delivery and rendering, leading to a more streamlined user experience. Below are a few advanced techniques for implementing lazy loading.
Lazy Loading for Videos and Iframes
Often videos and iframe embeds can be converted to clickable images. This ensures the heavyweight video files only load when explicitly requested by the user. Tools and plugins can automatically generate these previews, triggering media files to load only after user interaction.
For iframe embeds, especially for third-party content such as maps or social media feeds, lazy loading can significantly reduce initial load times. Leveraging API settings from these platforms can further streamline the process, ensuring that the lazy load behaves as intended.
Lazy Loading of Scripts
Loading scripts asynchronously can enhance performance for scripts that are non-essential during the initial page render. By categorizing scripts based on their priority and setting them to load conditionally, improve the perceived load time and interactivity of your web page.
Advanced Configuration and Troubleshooting
While basic implementations of lazy loading can be simple, larger or more complex sites might benefit from advanced configurations to tackle specific challenges, such as high traffic volumes, diverse device support, or unique content needs.
Choosing the Right Plugin Features
Select a lazy loading plugin that aligns closely with the needs of your site. Features such as conditional loading for mobile versus desktop, extensive element support, and compatibility with other plugins can make managing lazy loading seamless.
Ensuring Compatibility
It’s essential to test your site’s compatibility with lazy loading, especially after theme or plugin updates. Regularly browsing in different environments and utilizing testing tools can alert you to any issues that arise from conflicts or misconfiguration.
Using Performance Monitoring Tools
Online analysis tools such as GTmetrix and Web.dev provide insights into lazy loading efficiency. These tools can offer recommendations on optimizing image sizes, script placements, and detecting any unintentional blockages or errors.
Conclusion: Future of Lazy Loading
The future of web development heavily leans towards progressive enhancement and resource management techniques like lazy loading. Its significance will only grow as websites become richer in content. The integration of lazy loading capabilities signals a move towards a more efficient and user-centric web, and as technology evolves, so too will the tools and methods for implementing such strategies effectively. By staying informed about updates in browser support and ongoing improvements in lazy loading technologies, developers can continue to harness its benefits for faster, more efficient websites.